KEY THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY
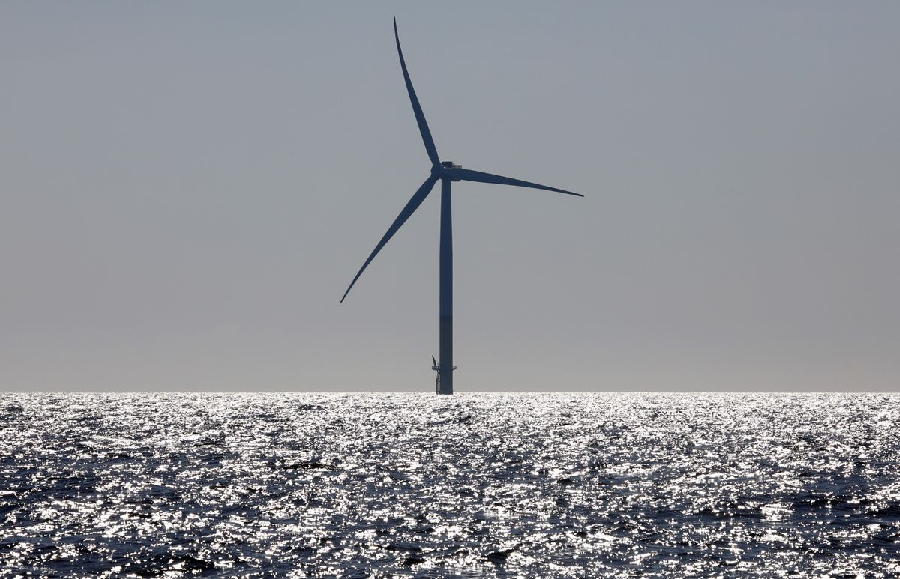

An offshore wind farm is a construction or power plant that harnesses high wind speeds converted to electricity and then fed into the electricity grid to supply energy. The most notable components of a wind farm are the wind turbines, the electrical cables, and the substations. Wind turbines are simply the structure that harnesses wind and converts it into electricity. Offshore wind farms installed further at sea to take advantage of intense wind speeds are increasingly becoming popular worldwide as countries strive to adopt clean and sustainable sources of energy. Here are the basic things you need to know about offshore wind energy.
Offshore wind energy is renewable.
The reason why offshore wind energy generation is increasingly growing is that wind is a renewable source of energy. Offshore wind farms are constructed in the sea to take advantage of the high wind speeds because of the absence of barriers, unlike on land. That means governments can meet their population’s growing energy demands, especially in the highly populated coastal cities and regions.
Offshore wind components are getting larger.
Offshore wind turbine components are getting larger with the ongoing innovations to construct even more powerful wind farms. Many of these components are transported by heavy ships and barges, minimizing some of the logistical challenges of using narrow roads or tunnels. Heavy lifting equipment and other construction tools are also necessary to enable engineers to build more powerful offshore wind farms to produce more electricity.
There are floating offshore turbines.
Currently, it is possible to construct floating offshore wind turbines. Latest innovations to reduce the challenges of the complex processes involved in fixing turbines in sea beds have come up. These floating foundations enable the construction of offshore wind platforms into deeper waters which means more energy generation.
Offshore wind farms use undersea cables.
Offshore wind farms use cables buried undersea to transmit electricity to the grid. The power generated by offshore wind farms must be transferred back to the land for use through cables buried in the sea beds. This electricity is channeled through coastal load centers and then distributed to the electrical grid to power homes and businesses.
Offshore wind turbines can be very tall.
It is possible to construct very tall offshore wind turbines to harness more wind power. It can be one and a half times the Washington monument’s height (over 500ft) with turbine blades the length of a football pitch.
Offshore wind energy comes at the right time.
Offshore wind energy is usually stronger during the day when energy needs are higher. That makes them a stable and efficient source of energy to run businesses and meet more energy demands. That is unlike most land-based wind turbines that produce more energy at night when energy demands are lower.
Offshore wind energy is environmentally friendly.
Unlike other energy sources such as burning coal and fossil fuels that can be harmful to human health and the environment, wind energy is clean and environmentally friendly. It does not emit toxic gases into the air that pollute the environment.
conclusion
As governments transition to renewable and clean energy sources, offshore wind farms will play a vital role in the future. Currently, many offshore wind farm constructions are underway to meet the high energy demands of populations globally.