Borobudur Temple as an Indonesian Tourist Attraction
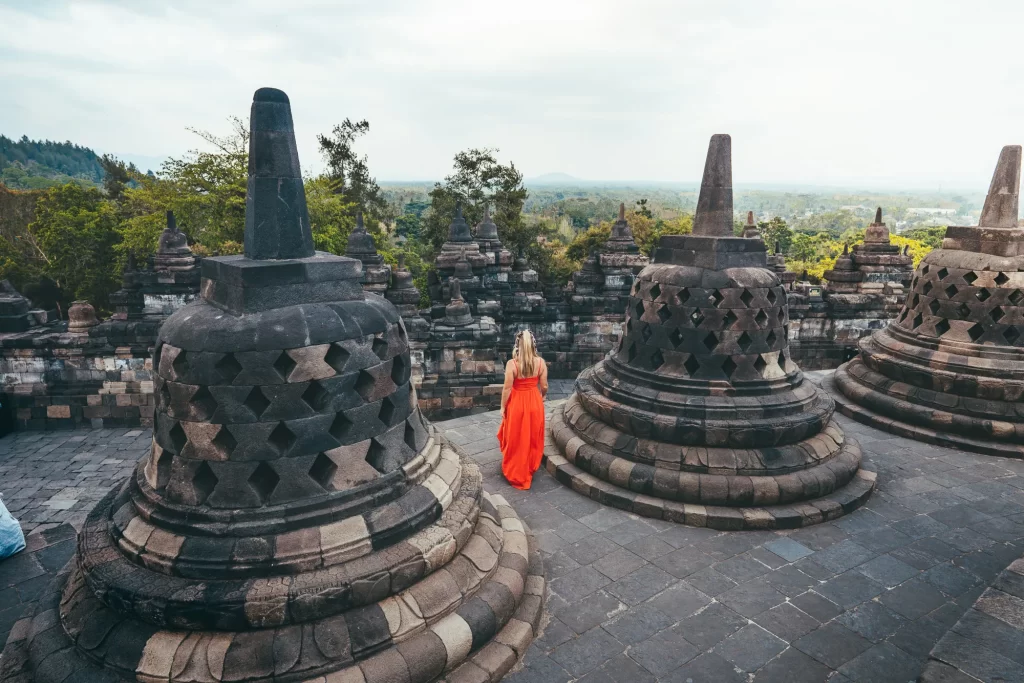

Borobudur Temple is a historical site located in Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia. This site is a tourist destination that must be visited when international tourists are on vacation in Indonesia. Borobudur Temple can be seen during the pandemic by implementing the indonesia quarantine rules.
Visitors are free to go on holiday to this temple as long as they comply with the health protocol. Various exciting spots are unique in Borobudur Temple. Here is some information that needs to be known before visiting the temple:
History of Borobudur Temple
Known as the largest Buddhist temple in the world, Borobudur was once crowned as one of the world wonders. Historically, Borobudur Temple was built around 750 AD or the 8th century. The construction process is estimated to take up to 75 years.
The structure of the building was destroyed by the eruption of Mount Merapi, which buried many parts of the temple. However, in the 1960s, the Indonesian government and UNESCO decided to rebuild Borobudur Temple.
The process of construction and renovation took a very long time. Many components must be studied by archaeologists to restore the shape of the temple like the original. Until 1991, Borobudur Temple was designated as a world heritage site.
Borobudur Temple Building Structure
After the completion of construction, Borobudur Temple began to open as a tourist attraction. Lots of local and foreign tourists who are interested in the Borobudur Temple Tour came to explore the whole temple area.
The structure of this temple building is shaped like a terrace, which is getting smaller with each step. Visitors can climb the stairs made from the original temple stone to get to the top.
It is about 121.66 meters long, over 35 meters high, and 121.38 meters wide. If you want to explore every corner of the temple, it takes a lot of energy because the area is extensive. But visitors can ride the train provided to get around the temple.
According to philosophers, the buildings at Borobudur Temple depict an imitation of the universe that symbolizes the wheel of life. There are three basic levels in the structure of the temple which have meaning separately as follow:
● Kamadhatu is the lowest part of the temple. This section describes human behavior as influenced by worldly desires.
● Rupadhatu is the middle part which describes the realm between. In nature, human behavior is not affected by worldly passions but is still tied to the real world.
● Arupadhatu is the top part of the temple, which is used as the embodiment of the upper world. According to Buddhist philosophy, in this realm, there are intangible elements that have left the world as a whole.
Indeed, one of the most famous tourist objects in the world is the Borobudur Temple. Many visitors from various regions and countries are still interested in visiting this site to this day. Tourists can enjoy the view of the temple while learning about the history of the kingdom in Indonesia.